|
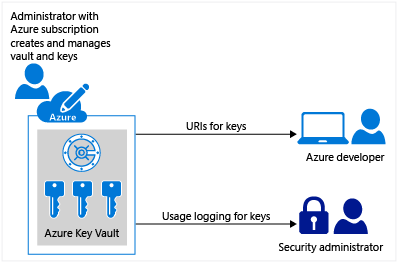
My customers are progressively embracing hybrid and multi-cloud environments to harness the advantages of a range of cloud platforms, including Microsoft Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud. While these configurations deliver unparalleled flexibility and scalability, they also bring about intricate cybersecurity hurdles. Within this blog, I will delve into the most effective strategies for fortifying hybrid and multi-cloud setups, with a particular emphasis on Microsoft Azure, to protect sensitive data and uphold a resilient cybersecurity stance. Best Practices for Securing Hybrid/Multi-Cloud Environments with Microsoft Azure:1. Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM): To ensure authorized access and prevent data breaches, utilize Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) for centralized identity management. Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to maintain fine-grained permissions. Regularly review and update user access privileges to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access. 2. Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest: Protecting data is paramount. Utilize SSL/TLS for data transmission between services and implement Azure Key Vault for secure key management. Employ Azure Disk Encryption to safeguard data at rest within virtual machines and Azure Storage, providing an additional layer of protection. Azure Key VaultAzure Key Vault is a cloud service that provides a secure store for secrets. You can securely store keys, passwords, certificates, and other secrets. Azure key vaults may be created and managed through the Azure portal. Azure Key Vault offers the following features:
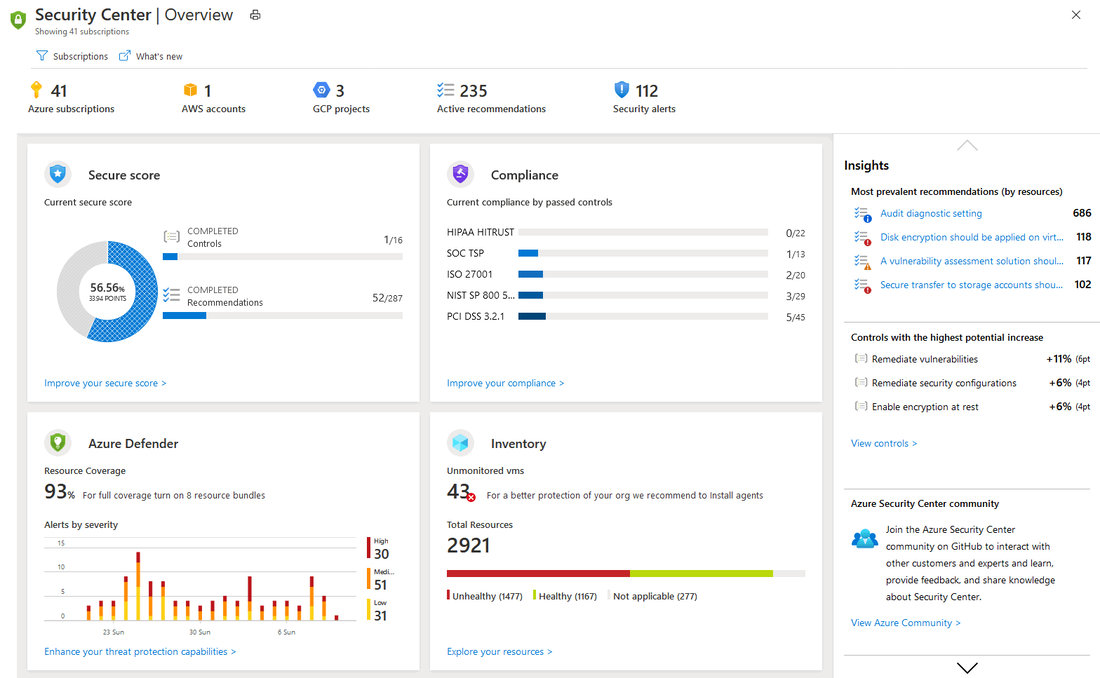
3. Network Security and Segmentation: Establish a secure network environment using Network Security Groups (NSGs) and Azure Firewall to control traffic flow between virtual networks and subnets. Leverage Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) or ExpressRoute for encrypted and private connections between on-premises and Azure resources, mitigating the risk of data interception. 4. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection: Stay vigilant by enabling Azure Security Center to monitor and detect threats across your Azure resources. Leverage Azure Monitor, Azure Log Analytics, and Azure Network Watcher for real-time monitoring and rapid incident response, ensuring timely action against potential security breaches. Azure Security CenterAzure Security Center (ASC) is a unified infrastructure security management system that provides a comprehensive view of your security posture across your Azure resources. It helps you identify and mitigate security risks, improve your compliance posture, and stay ahead of threats. ASC provides the following key capabilities:
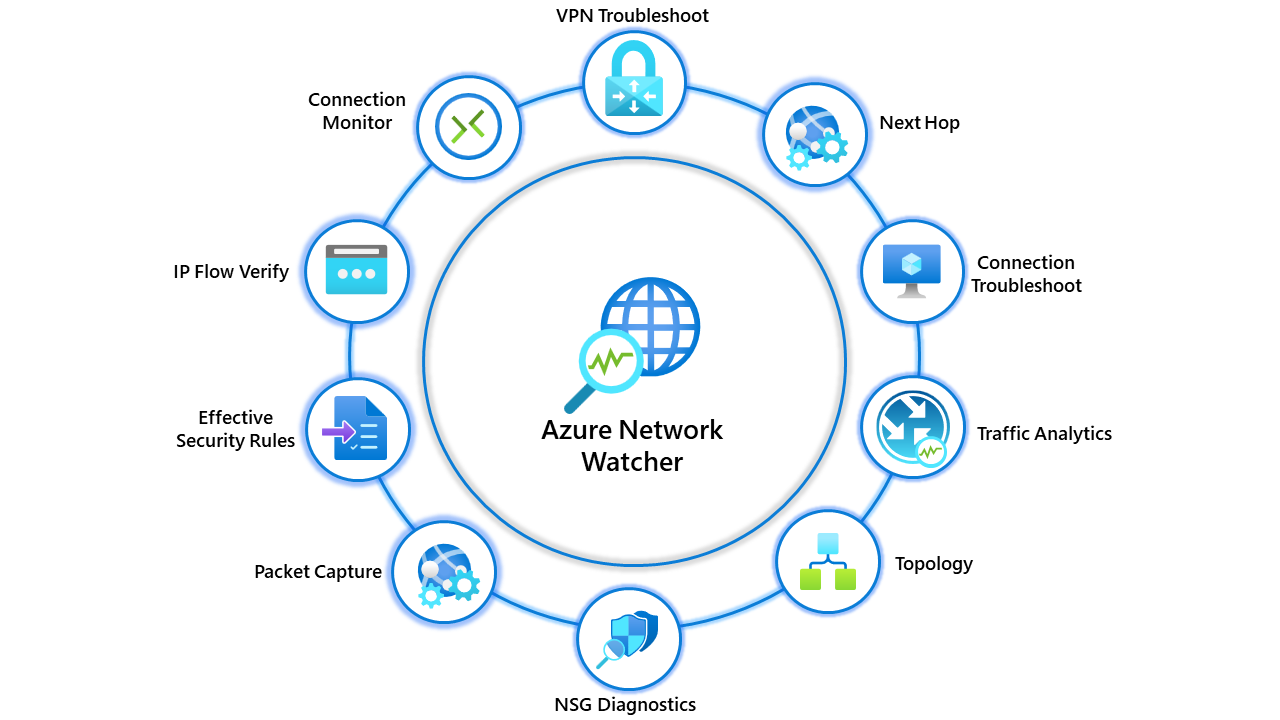
Azure Network WatcherAzure Network Watcher is a service that helps you monitor, diagnose, and analyze your Azure networks. It provides a variety of features, including:
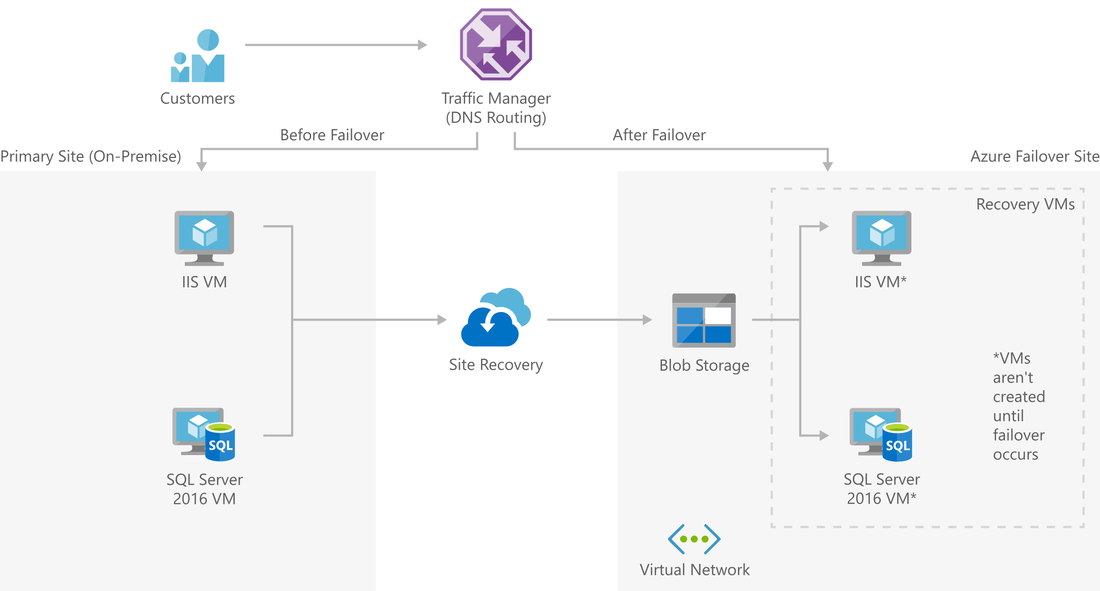
5. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Plan for unforeseen events with a robust disaster recovery strategy. Implement Azure Site Recovery to ensure business continuity by replicating and recovering Azure resources across regions. Additionally, utilize Azure Backup for regular data backups to enable swift recovery in case of data loss Azure Site RecoveryAzure Site Recovery (ASR) is a disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) solution that helps you protect your on-premises workloads by replicating them to Azure. It can be used to protect a wide range of workloads, including virtual machines, physical servers, and applications. ASR offers the following key features:
6. Compliance and Governance: Enforce compliance and security standards for your Azure resources using Azure Policy. Ensure consistent and compliant cloud environments by adopting Azure Blueprints, streamlining governance across your organization's cloud deployment. 7. Security Automation and Orchestration: Boost your security operations by integrating automation tools such as Azure Logic Apps and Azure Functions. Streamline incident response and threat detection by leveraging Azure Security Center integrated with Azure Sentinel for advanced security orchestration and response. Azure Logic Apps and Azure FunctionsAzure Logic Apps and Azure Functions are both serverless platforms that can be used to automate tasks and build applications. However, they have different strengths and weaknesses, and are suited for different use cases. Azure Logic Apps is a workflow automation service that allows you to create automated workflows that connect different applications and services. Logic Apps can be used to automate a wide variety of tasks, such as:
Azure Functions is a compute service that allows you to run code in response to events. Functions can be used to perform a variety of tasks, such as:
8. Regular Security Audits and Reviews: Conduct periodic security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure adherence to security policies. Stay proactive by continuously reviewing and updating security configurations to address evolving threats and compliance requirements. 9. Employee Training and Awareness: Equip your team with Azure-specific security knowledge through regular training programs. Cultivate a security-conscious culture, encouraging employees to promptly report security incidents and fostering a strong security mindset. 10. Stay Informed About Security Updates and Patches: Keep track of security updates and patches released by Azure and other cloud providers. Implement updates promptly to mitigate known vulnerabilities and stay ahead of potential security risks. 11. Limit Exposed Attack Surfaces: Minimize the attack surface by closing unnecessary ports and services on virtual machines and containers. Regularly assess and reduce the use of public-facing IPs and services, reducing potential points of entry for attackers. 12. Regularly Test Security Measures: Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify weaknesses in the cloud environment. Perform red team-blue team exercises to simulate attacks and test the effectiveness of incident response procedures. Securing hybrid/multi-cloud environments, with a focus on Microsoft Azure, requires a holistic approach that combines technical measures, organizational policies, and constant vigilance. By adhering to these best practices, organizations can establish a strong security foundation, protect sensitive data, and confidently leverage the benefits of Azure and other cloud platforms in their digital journey.
Emphasizing security not only mitigates risks but also cultivates customer trust and confidence in cloud-based services, ensuring a successful and secure cloud adoption. With continuous monitoring, regular updates, and employee awareness, organizations can navigate the dynamic cybersecurity landscape and master security in their hybrid/multi-cloud deployments.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
RecognitionCategories
All
Archives
June 2024
|









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed