|
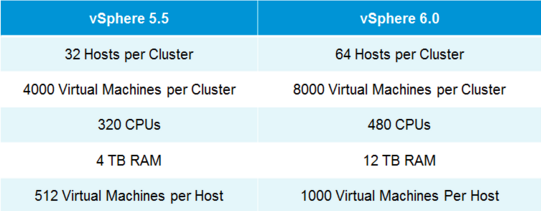
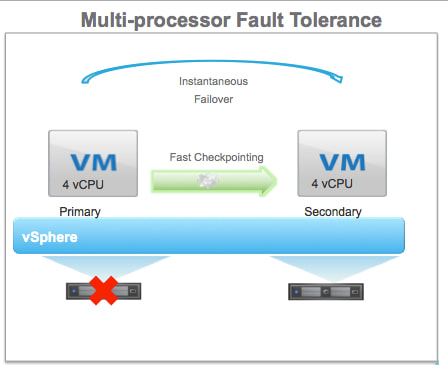
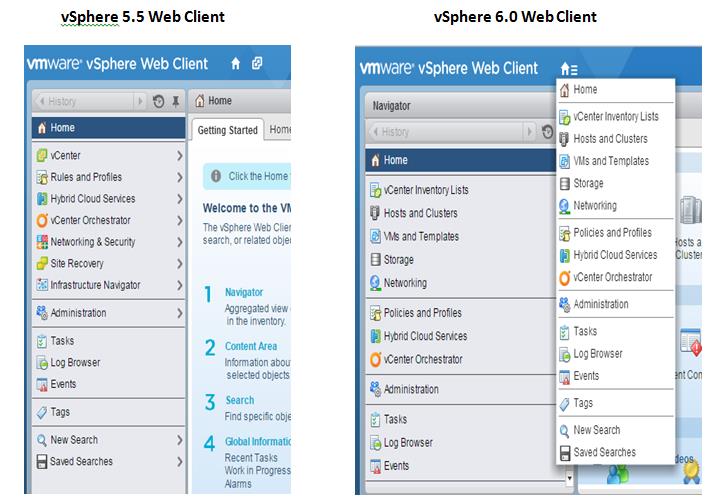
VMware vSphere 6.0 is the next major release since 5.5 and with any major release it is packed with new features and enhancements along with increased scalability. This version comes with some big improvements to VSAN which I'll discuss below. Host ImprovementsIn vSphere 5.5 the maximum supported host memory was 4TB, in 6.0 that jumps up to 12TB. Also, in vSphere 5.5 the maximum supported number of logical (physical) CPUs per host was 320 CPUs, in vSphere 6.0 that is increased to 480 CPUs. The last improvement to the hosts is the maximum number of VMs per host, increasing from 512 in 5.5 to 1000 VMs per host in 6.0 This gives the ability to create some monster VMs. Fault Tolerance IprovementsFault Tolerance (FT) was introduced in vSphere 4. FT provides protection of VMs by preventing downtime in case of a host failure. FT has never been greatly used due to its design preventing anyone that required multiple CPUs from utilizing FT. FT now supports more than one vCPU and moves from 1 vCPU to 4 vCPU support. The design of FT has changed were the way FT worked in the past you had 2 VMs on separate hosts, one as a primary and the other as the secondary. The VMs relied on shared storage. In vSphere 6.0 this has now changed allowing for each VM to have their own virtual disk that can be located on different storage. VMware also improved the prior limitations with snapshot support for FT. Having separate disks helped with this issue. Now that there is built in support for snapshotting a FT VM, you can back it up. Prior to this admins found themselves challenged with how to perform agentless backup while maintaining FT for the VMs requiring it. In order to backup the VMs requiring FT prior to 6.0 you had to install a backup agent and backup the vm in a more traditional manner. vSphere Web Client ImprovementsThe web client has never been a favorite of admins and with the release of vSphere 6.0 VMware has made some great performance and usability improvements. Performance Improvements:
Usability Improvements:
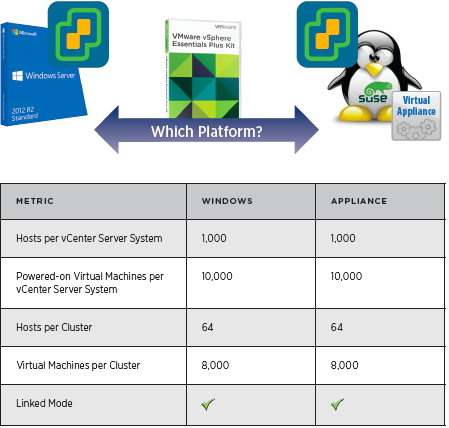
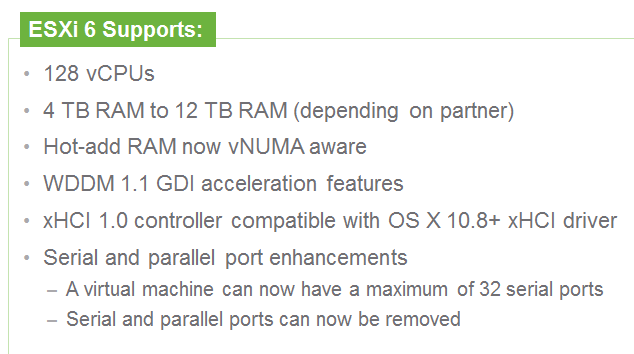
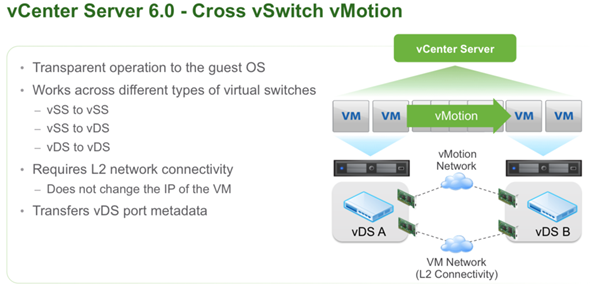
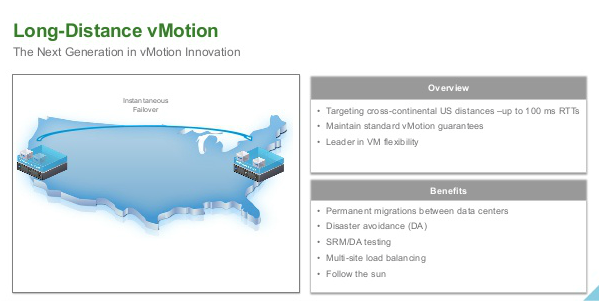
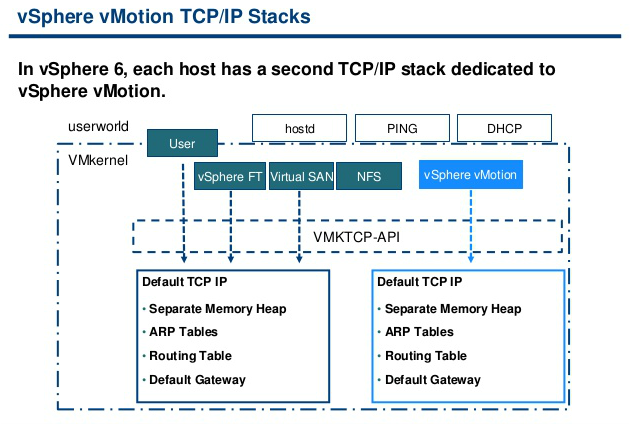
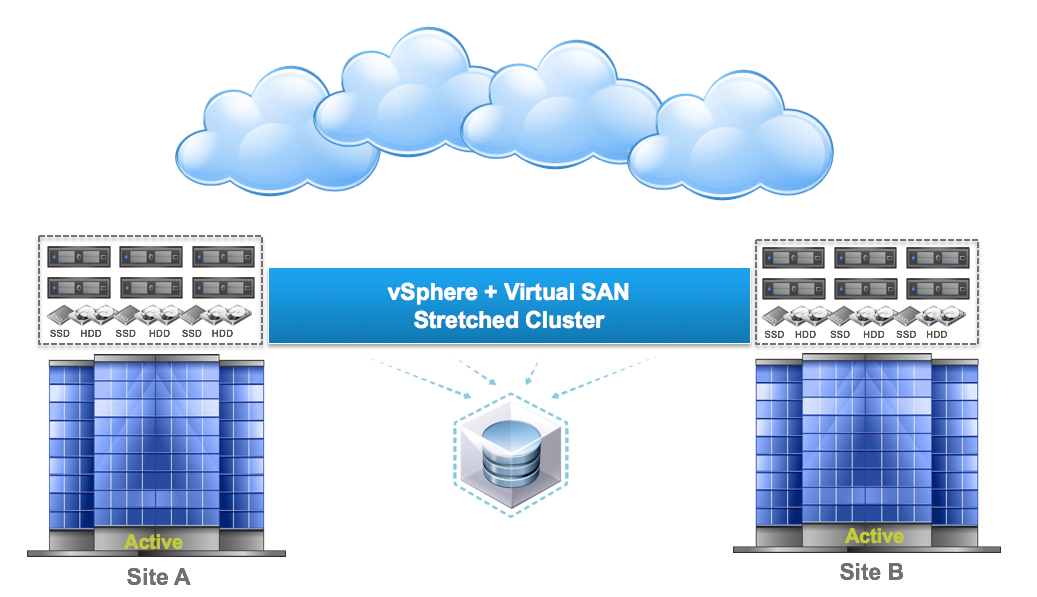
vCenter Server Appliance ImprovementsI have never been a fan of having to burn Microsoft Licenses in order to deploy vCenter or the amount of time it takes to spin up a Windows OS to support it for both the application and SQL database. I loved it when VMware came out with the appliance for an easy ova deployment but the limitations in scalability and support have been the main driving factor for admins to not deploy this in their environments. now in vSphere 6.0 the VCSA is fully scalable to the same limits that the vCenter Server on Windows scales to. This now means that the VCSA can support 1,000 hosts, 10,000 VMs and now linked mode. VM Improvements in 6.0Back in vSphere 5.5 a VM could be configured with up to 64 vCPUs and now in 6.0 that maximum has doubled to 128 vSPCUs. That is a crazy amount of vCPU. Another increase for the VM is around serial ports. VMware saw a need for this and has increased from 4 to 32 ports that can be configured on a single VM. If you don't have a need for them then you can remove the serial ports and parallel ports as needed. vMotion!!There have been a lot of new enhancements with vMotion technology to increase the range and capabilities of vMotioning a VM. You can now vMotion a VM between different types of virtual switches. VMs can be moved from a Standard vSwitch to a Distributed vSwitch without changing its IP address and without network disruptions. With the improvements to vMotion you can now vMotion a VM from a host located in one vCenter server to another host on a different vCenter server. There is no need for common shared storage between the the hosts and vCenter servers. This eliminates the traditional distance boundaries of vMotion. You can now move between data centers, regional data centers or continental. Another improvement to vMotion resides around latency requirements. In vSphere 5.5 the maximum vMotion latency was 10ms. In vSphere 6.0 that has increased to 100ms of latency. This allows for the vMotion of VMs between longer distances. VMware vMotion also includes its own TCP/IP stack which can cross layer 3 networks. Single Sign-on Improvementsn vSphere 6.0 VMware introduces a new Platform Services Controller. The controller groups together SSO, Licensing and Certificate authority. You can deploy this as embedded with vCenter server or external so that is completely independent of the vCenter server. Certificate management has always been a pain for Administrators. With the introduction of VMCA, you can now manage the provisioning and deployment of certificates for you vCenter servers, and ESXi hosts. vSANNow in its 3rd release as of August of 2015, VSNA 6.1 has already seen adoption across different industries and sizes. This release adds abilities around availability data protection and management. Virtual SAN Stretched Cluster allows admins to create a stretched cluster between two or more geographically separated data centers. Another feature of this release is Virtual SAN for Remote Office or Branch Offices. This provides the ability to deploy VSAN clusters for ROBO. You can now deploy large numbers of 2-node VSAN clusters that can be centrally managed from a central data center through one vCenter server.
Some other new features include:
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
RecognitionCategories
All
Archives
April 2024
|












 RSS Feed
RSS Feed