|
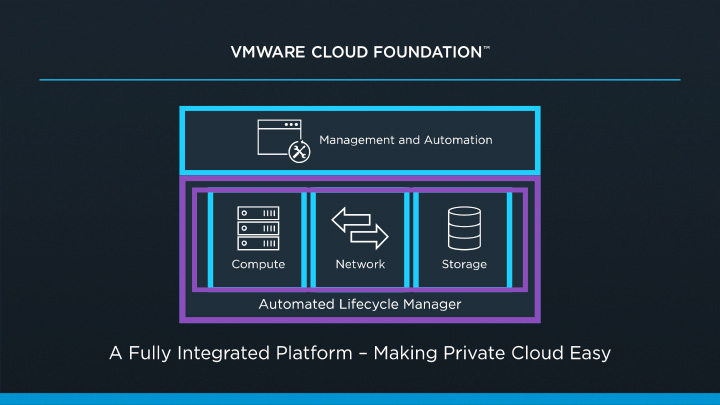
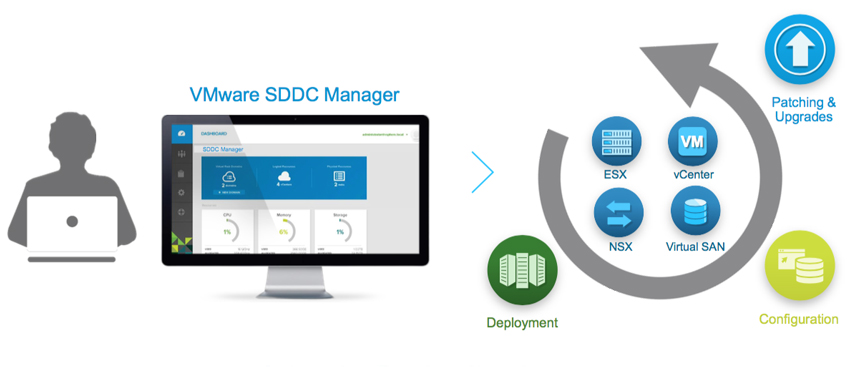
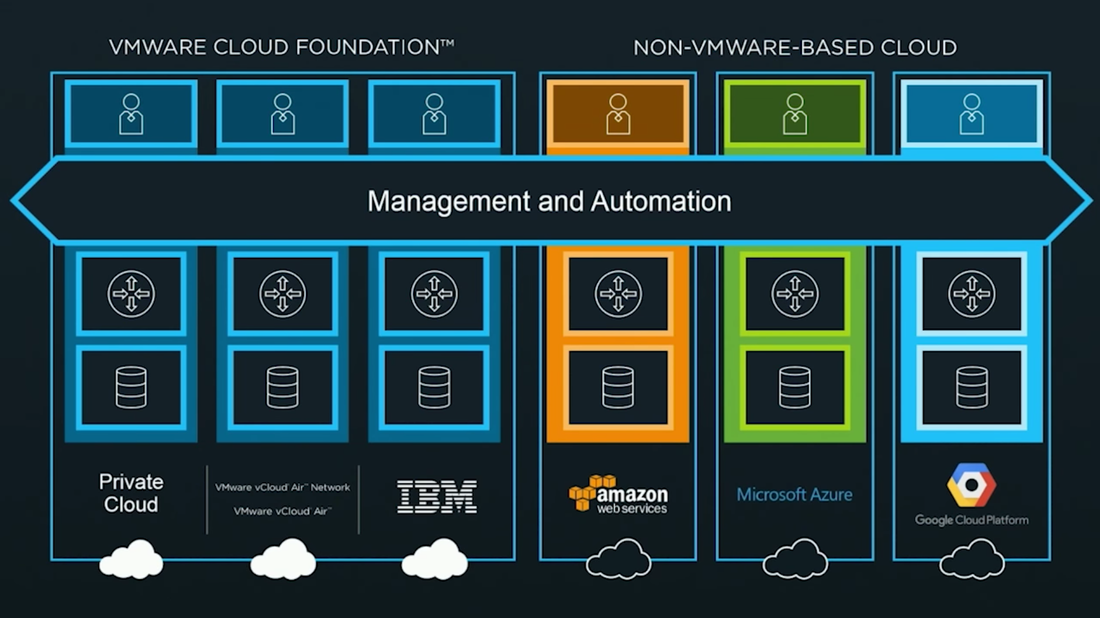
VMware announced VMware Cloud Foundation back in the general session of VMworld 2016. Cloud Foundation is a unified platform for private and public clouds. Let's start with defining the term "Clouds". This term has been thrown around a lot and some take this term as "In the Cloud" off premises platforms, but some use the term more all inclusive which includes both "On-Prem" and "Off-Prem" platforms. Wikipedia defines this term as "computing that provides shared computer processing resources and data to computers and other devices on demand". For this blog I am using the definition of cloud as the latter. I think of cloud as all inclusive of both off and on-prem platforms for providing resources. I know some feel as though cloud was meant to replace the "on-prem" private cloud and yes, that will ultimately be the direction in years to come, but for now we live in a world of hybrid-cloud and that is what Cloud Foundation is here to assist us with. Now that we have cleared that up, let's move on to Cloud Foundation from VMware. Cloud Foundation brings together, VMware's vision for SDDC where compute, storage, and networking services are decoupled from the underlying hardware and abstracted into software as pools of resources allowing for IT to become more flexible and agile while also allowing for better management, into an integrated stack for cloud. This is done by defining a platform common to both private and public clouds. The foundational components of Cloud Foundation are VMware vSphere, Virtual SAN, and NSX and can be packaged with vRealize Suite to bring automation into the picture. If you are not familiar with the vRealize Suite from VMware let's just take a moment to discuss this. The vRealize Suite is a software defined product suite built to enable IT to create and manage hybrid clouds. It includes products like IT Business Enterprise, which VMware just sold off, and is an IT financial management tool to manage and analyze cost associated with IT services. It also includes vCloud Automation Center, vCenter Operations Management, and LogInsight. The management for Cloud Foundation is VMware's SDDC Manager. SDDC Manager serves as a single interface for managing the infrastructure. From this interface, the IT administrator can provision new cloud resources, monitor changes to the logical infrastructure, and manage lifecycle and other operational activities. The idea here is a single pane of glass for management along with monitoring of all your cloud environments whether it be on-prem, IBM-Cloud, AWS, etc., providing ongoing performance management, capacity optimization, real-time analytics, and cloud automation. Cloud Foundation allows for a flexible solution allowing for on-prem and off-prem deployment options and can be deployed on-prem or off-prem as a service. You can choose on-prem options like integrated solutions from OEM providers such as VCE with hyper-converged systems and VSAN ready nodes from Dell. Cloud Foundation will help to reduce the complexities faced with cloud strategies to date. The idea of "who cares where your data resides as long as it it secure and accessible" comes to mind. You can have applications being delivered from multiple clouds whether on or off-prem, Azure, or AWS. IT only needs a single pane of glass to monitor and manage these environments while also allowing for IT and management to track related costs. Ultimately giving IT the agility of migrating between cloud platforms when needed. A use case for this would be a merger and acquisition of a company with a hybrid cloud environment. Cloud Foundation would help manage the complexities involved with integrating those resources into your own environment while maintaining security and the integrity of your current environment. VMware announced alongside the Cloud Foundation announcement at VMworld 2016 the new partnership with IBM Cloud. This allows companies to have choice in deploying SDCC whether it be on-prem in their own private data center(s) or with IBM. This solution is based with Cloud Foundation and allowing VMware customers to seamlessly extend private to public. Again, the software stack includes VMware vSphere, Virtual SAN, NSX, and VMware SDDC Manager. VMware SDDC Manager was announced back at VMworld 2015 and combined with Cloud Foundation is just the next step toward IoT with what VMware states as "Any Cloud, Any Application, Any Device". The SDDC Manager allows for a simplified management of a highly distributed architecture and resources. Cloud foundation integrates with the entire VMware stack which includes Horizon, vRealize Suite, vRealize Automation, vRealize Business, OpenStack and products like LogInsight. With Cloud Foundation natively integrating the software-defined data center stack and SDDC Manager, customers can flexibly upgrade individual components in the stack to higher editions allowing for flexibility in lifecycle management which consumes large amount of time in traditional IT. With Cloud foundation you can automate the entire software stack. Once the rack is installed and powered on with networking to the rack, the SDDC Manager takes the BOM that was built with your partner like Advizex, and includes user-provided environmental information like DNS, IP addresses, etc. to build out the rack. The claim is that this can reduce the provisioning time from weeks to hours which for those of you that have done this in a non-automated fashion can attest to how painful the process can be. When complete you have a virtual infrastructure ready to start deploying and provisioning workloads. In the complexities of traditional IT with silos, it takes extensive resources to provision a highly available private clouds, but with Cloud Foundation an administrator only needs to create and manage pools of resources decreasing the time to delivery of IT resources for consumption by the end-user whether it be a vm or a virtual desktop. This is done through a new abstraction layer called, Workload Domains. Workload Domains are a policy-driven approach for capacity deployment. Each workload domain provides the needed capacity with specified policies for performance, availability and security. An admin can create a workload for dev/test with a balanced performance and low availability requirement while also creating one for production with high availability and high performance. The SDDC Manager translates these policies into the underlying resources of compute which allows for the admin to concentrate on higher level tasks instead of spending time researching how to best implement. Lifecycle management introduces a lot of complexities which are typically manual process to patch and upgrade and can lead to issues within an infrastructure due to interoperability and configuration errors. In turn the validation and testing of these patches takes a lot of time away from an IT staff. Sometimes patches get deployed before they have been vetted correctly for security and other reasons or defer patches which can slow down the roll-out of new features, etc. SDDC Manager automates these tasks for both physical and virtual infrastructures. VMware tests all the components for the Cloud Foundation before shipping new patches to the customer. Within the lifecycle management of Cloud Foundation you can choose to apply the patches to just certain workloads or the entire infrastructure. SDDC can patch the vms, servers and switches while maintaining uptime thereby freeing resources to focus on business critical initiatives. Scalability is built into the platform within a hyper-converged architecture. You can start with a deployment as small as 8 nodes, and scale to multiple racks. Capacity can be added linearly in increments as small as one server node at a time within each rack allowing IT to align CapEx with business needs. Cloud Foundation automatically discovers any new capacity and adds it into the larger pool of available capacity for use. Some main use cases for Cloud Foundation are; Virtual Infrastructure allowing IT to expand and contract the underlying infrastructure to meet their changing business needs; IT Automating IT allowing IT accelerate the delivery and ongoing management of infrastructure, application and custom services, while improving overall IT efficiency; Virtual Desktop making VDI deployments faster and more secure. Administrators can focus on specifying the policies and needs of the VDI infrastructure instead of dealing with the details of deploying the VDI infrastructure. To learn more about VMware's Cloud Foundation you can visit the product page here.
You can also get hands-on with the product from the hands-on lab provided online from VMware. HOL-1706-SDC-5 - VMware Cloud Foundation Fundamentals
1 Comment
Back in July of 2016, VMware issued a Field Advisory, announcing bugs for the release of NSX for vSphere 6.2.3. VMware urged its user community, not to upgrade to this version and if you had they came out with a 6.2.3.a release to resolve the issues. The issues that VMware found were that both primary and secondary HA nodes would be placed into Active State, causing network disruption and issues related to the DFW rules causing traffic disruptions.
VMware has now released, back in August, the new version 6.2.4 for GA. This release includes some critical bug fixes previously identified which includes a critical input validation vulnerability for sites that use NSX SSL VPN. You can see the full list what's new in the release notes. Most of the new features were already discussed by me in a previous post you can find here. In this new version the only thing listed as new is a new feature around "Firewall Status API". VMware also has announced the End of Availability (EOA) and End of General Support (EOGS) for Cloud Networking and Security 5.5.x. The date is September 19, 2016 for both. You can see a list of NSX trending issues here. |
RecognitionCategories
All
Archives
April 2024
|












 RSS Feed
RSS Feed