|
In the current landscape shaped by Broadcom's influence on VMware's trajectory, organizations considering staying with VMware might find it prudent to explore transitioning to a hybrid cloud setup. Opting for the right infrastructure becomes paramount to ensure optimal performance and scalability. Among the offerings in the revamped portfolio, VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) emerges as a favored option, thanks to its robust software-defined data center (SDDC) capabilities. Amid Broadcom's streamlined portfolio, featuring VMware vSphere Foundation and VMware Cloud Foundation, loyal VMware customers have a compelling incentive to opt for a dedicated solution. Combining VCF with Dell VxRail presents an attractive proposition. Not only is VxRail custom-built for VCF, but it also offers the flexibility to integrate third-party storage alongside VMware vSAN. This is important for customers who have investments that are already made in existing external storage systems or have a use case in which external storage systems are required. This combination sets itself apart with its seamless integration, streamlined management, and enhanced performance. Consequently, deploying VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell VxRail emerges as the prime selection. Tailored Integration and OptimizationDell VxRail is specifically designed with VMware environments in mind, which makes it an ideal platform for VMware Cloud Foundation. The integration goes beyond general compatibility; Dell VxRail comes pre-configured with VMware vSAN and is fully optimized for VMware environments. This deep integration allows businesses to leverage a hyper-converged infrastructure that simplifies and streamlines deployment, management, and scaling of VMware-based applications. Simplified Deployment and ManagementOne of the standout features of running VCF on VxRail is the simplified deployment process. VxRail Manager, along with VMware SDDC Manager, provides a unified management experience that automates the deployment and configuration of VMware components. This integration reduces the complexity typically associated with setting up a hybrid cloud environment, enabling IT teams to focus more on strategic operations rather than routine setups. Scalability and FlexibilityScalability is a critical consideration for organizations aiming to thrive in a dynamic market. VxRail presents a scalable architecture that evolves alongside your business requirements. Whether expanding vertically or horizontally, VxRail offers the flexibility to incorporate additional nodes or integrate new technologies seamlessly, preserving ongoing operations. This adaptability empowers organizations to extend their VMware Cloud Foundation environment in a cost-effective and efficient manner. Additionally, as part of scalability, customers can seamlessly extend to hybrid cloud offerings by VMware such as VMware Cloud on AWS or the Azure VMware Solution, further enhancing flexibility and agility. Enhanced Performance and ReliabilityRunning VCF on Dell VxRail brings the advantage of optimized performance. VxRail nodes are equipped with high-performance processors and memory options, tailored for data-intensive applications that are typical in VMware environments. Moreover, Dell’s proactive support and single-point-of-contact service significantly enhance the reliability of the infrastructure, ensuring high availability and minimal downtime. Streamlined Support and ServicesChoosing Dell VxRail for running VMware Cloud Foundation simplifies the support process. Since Dell and VMware are closely partnered, VxRail comes with integrated support for both hardware and software components. This means quicker resolution of issues and less downtime, which is crucial for maintaining continuous business operations. The cohesive support structure is a significant advantage for IT departments that manage complex environments. Final ThoughtsFor businesses leveraging VMware Cloud Foundation, Dell VxRail serves as a synergistic platform that enhances VCF's capabilities through superior integration, simplified management, scalability, optimized performance, and streamlined support. This amalgamation not only boosts the efficiency of VMware deployments but also provides a resilient infrastructure supporting business growth and technological advancement. Moreover, with Broadcom's streamlined portfolio featuring VCF, customers committed to VMware environments find compelling reasons to opt for this integration. Dell VxRail's compatibility with third-party storage solutions alongside VMware vSAN offers unparalleled flexibility, making it an ideal choice for enterprises seeking to optimize their hybrid cloud strategy while retaining the ability to tailor their storage requirements. Alongside these benefits, incorporating cloud offerings such as VMware Cloud on AWS or the Azure VMware Solution enhances scalability and agility, enabling organizations to seamlessly extend their VMware environment to the cloud. For organizations seeking to maximize their VMware infrastructure, running VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell VxRail presents a strategic and operationally advantageous choice, offering substantial benefits for both current and future needs. References
0 Comments
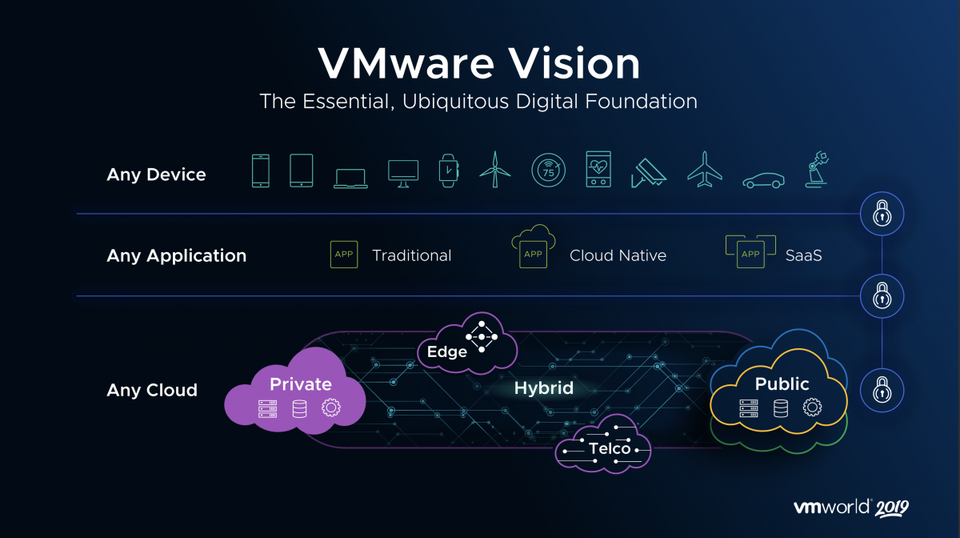
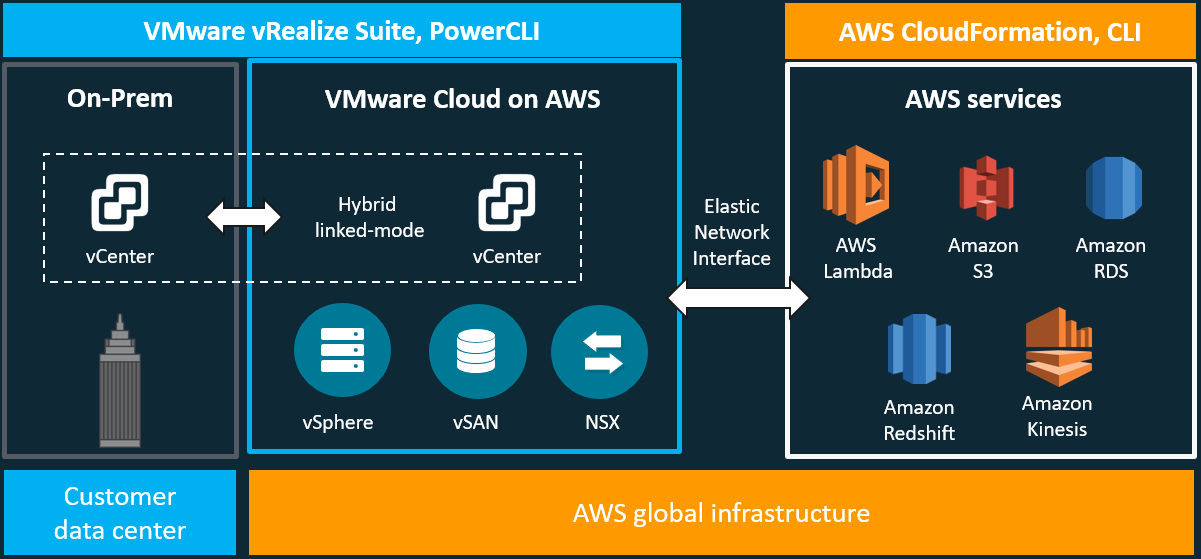
I wrote a blog about this subject before, which can be found here. The information contained in that blog is still relevant to this conversation and walks you through the challenges for traditional three-tier architecture and how the industry, specifically VMware, has addressed those challenges. In this blog, I will be updating the vision that VMware has laid out for the hybrid-cloud, which is comprised of VMware Cloud on AWS and VMware Cloud Foundations. To better understand this journey and how we have arrived at this vision of Any Device, Any Application, and Any Cloud, take a look back at the previous blog. Let's begin with an overview of VMware Cloud on AWS. Quick Overview of VMware Cloud on AWSVMware Cloud on AWS is a jointly engineered and integrated cloud offering developed by VMware and AWS. Through this hybrid-cloud service, organizations can deliver a stable and secure solution to migrate and extend their on-premises VMware vSphere-based environments to the AWS cloud running on bare metal Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) infrastructure.
VMware Cloud on AWS has several use case buckets that most customers find themselves falling into some overlap. The first of these use cases is for organizations looking to migrate their on-premises vSphere-based workloads and to extend their capacities to the cloud with the data center extension use case. The next, is for organizations looking to modernize their recovery options, new disaster recovery implementations, or organizations looking to replace existing DR infrastructure. The last one that I will mention, is for organizations looking to evacuate their data centers or consolidate data centers through cloud-migrations. This is great for organizations looking at data center refreshes. VMware Cloud on AWS is delivered, sold, and supported by VMware and its partners like Sirius Computer Solutions, a Managed Service Partner. Available in many AWS Regions which can be found here and growing. Through this offering organizations can build their hybrid solutions based on the same underlying infrastructure that runs on VMware Cloud on AWS, VMware Cloud Foundations. Day 1 began with the general session, which was a lot different than the previous year where the VMware Executives laid out their vision for the partner community. This general session was focused more correctly on the audience in attendance.
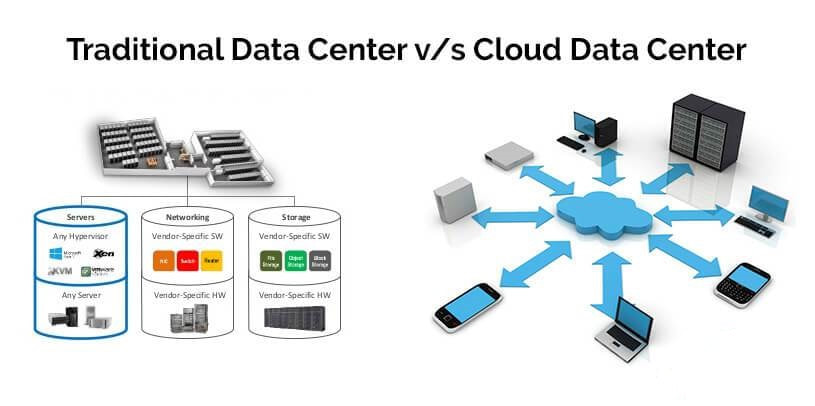
The movement toward a hybrid cloud, software defined data center, has been on-going for years now. We have seen the virtualization of compute, storage, and now networking. In this blog, I will be discussing this journey: where we started, where we are going, and why you want to be on this journey. Traditional data center models are still very prevalent and accepted by organizations as the defacto model for their data center(s). If you have ever managed a traditional data center model, then you know the surmounting challenges we face within this model.
What comprises the traditional data center model? A traditional data center model can be described as heterogeneous compute, physical storage, and networking managed by disperse teams all with a very unique set of skills. Applications are typically hosted in their own physical storage, networking, and compute. All these entities-physical storage, networking, and compute- increase with the growth in size and number of applications. With growth, complexity increases, agility decreases, security complexities increase, and assurance of a predictable and repeatable production environment, decrease. Characterizations of a Traditional Data Center:
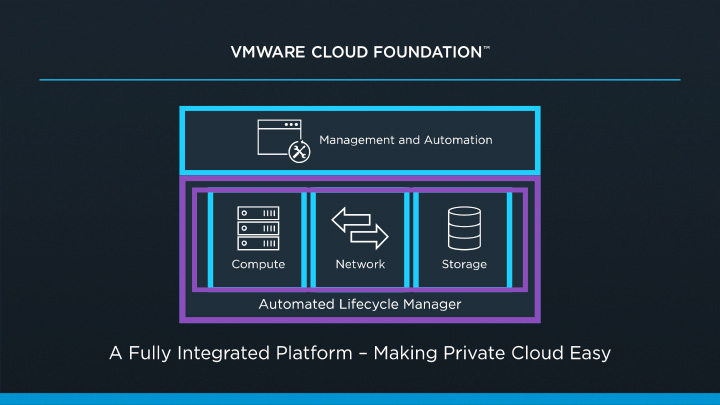
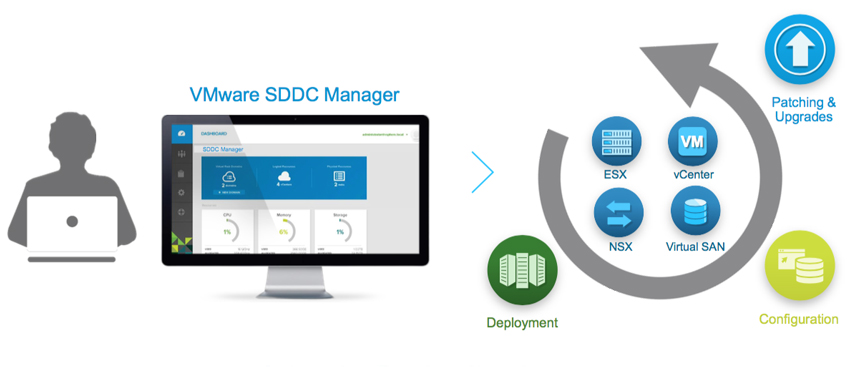
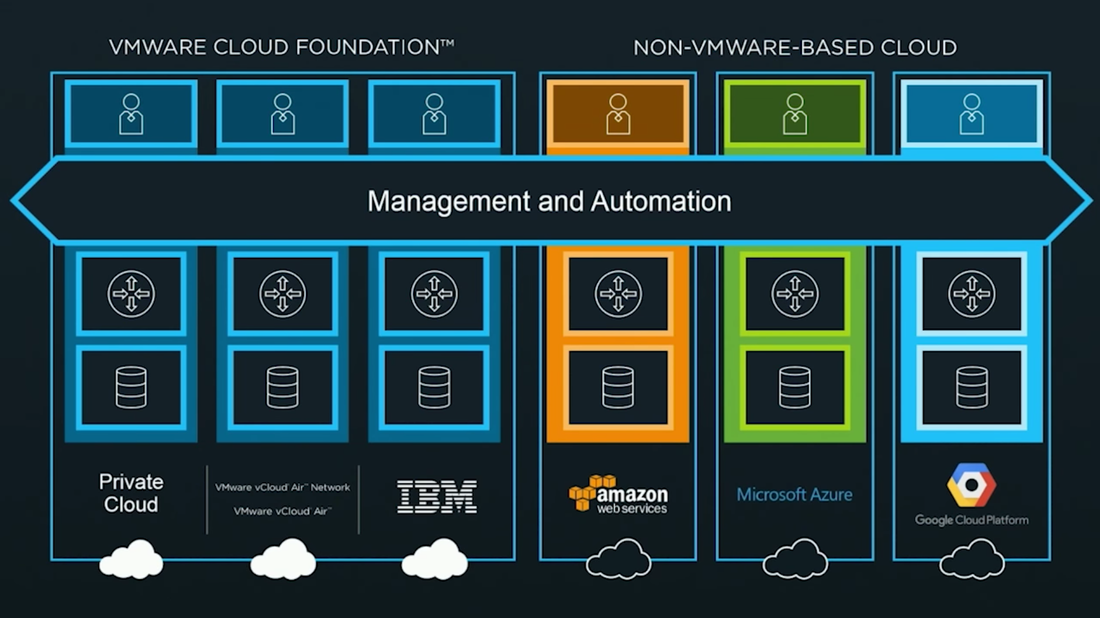
Challenges around supporting these complex infrastructures can include things like slow time to resolution when an issue arises due to the complexities of a multi-vendor solution. Think about the last time you had to troubleshoot a production issue. In a typical scenario, you are opening multiple tickets with multiple vendors. A ticket with the network vendor, a ticket with the hyper-visor vendor, a ticket with the compute vendor, a ticket with the storage vendor, and so on and so on. Typically, all pointing fingers at each other when we all know that fault always lies with the database admins. The challenges aren't just around the complexities of design, day to day support, or administration, but also include challenges around lifecycle management. When it comes to lifecycle management, we are looking at the complexities around publishing updates and patches. If you are doing your due diligence, then you are gathering and documenting all the firmware, bios, and software from all the hardware involved for the update/patch and comparing that information against Hardware Compatibility Lists and Interoperability Lists to ensure that they are in a supported matrix. If not, then you have to update before going any further. This can be extremely time consuming and we are typically tasked with testing in a lab that doesn't match our production environment(s) ensuring we don't bring any production systems down during the maintenance window. VMware announced VMware Cloud Foundation back in the general session of VMworld 2016. Cloud Foundation is a unified platform for private and public clouds. Let's start with defining the term "Clouds". This term has been thrown around a lot and some take this term as "In the Cloud" off premises platforms, but some use the term more all inclusive which includes both "On-Prem" and "Off-Prem" platforms. Wikipedia defines this term as "computing that provides shared computer processing resources and data to computers and other devices on demand". For this blog I am using the definition of cloud as the latter. I think of cloud as all inclusive of both off and on-prem platforms for providing resources. I know some feel as though cloud was meant to replace the "on-prem" private cloud and yes, that will ultimately be the direction in years to come, but for now we live in a world of hybrid-cloud and that is what Cloud Foundation is here to assist us with. Now that we have cleared that up, let's move on to Cloud Foundation from VMware. Cloud Foundation brings together, VMware's vision for SDDC where compute, storage, and networking services are decoupled from the underlying hardware and abstracted into software as pools of resources allowing for IT to become more flexible and agile while also allowing for better management, into an integrated stack for cloud. This is done by defining a platform common to both private and public clouds. The foundational components of Cloud Foundation are VMware vSphere, Virtual SAN, and NSX and can be packaged with vRealize Suite to bring automation into the picture. If you are not familiar with the vRealize Suite from VMware let's just take a moment to discuss this. The vRealize Suite is a software defined product suite built to enable IT to create and manage hybrid clouds. It includes products like IT Business Enterprise, which VMware just sold off, and is an IT financial management tool to manage and analyze cost associated with IT services. It also includes vCloud Automation Center, vCenter Operations Management, and LogInsight. The management for Cloud Foundation is VMware's SDDC Manager. SDDC Manager serves as a single interface for managing the infrastructure. From this interface, the IT administrator can provision new cloud resources, monitor changes to the logical infrastructure, and manage lifecycle and other operational activities. The idea here is a single pane of glass for management along with monitoring of all your cloud environments whether it be on-prem, IBM-Cloud, AWS, etc., providing ongoing performance management, capacity optimization, real-time analytics, and cloud automation. Cloud Foundation allows for a flexible solution allowing for on-prem and off-prem deployment options and can be deployed on-prem or off-prem as a service. You can choose on-prem options like integrated solutions from OEM providers such as VCE with hyper-converged systems and VSAN ready nodes from Dell. Cloud Foundation will help to reduce the complexities faced with cloud strategies to date. The idea of "who cares where your data resides as long as it it secure and accessible" comes to mind. You can have applications being delivered from multiple clouds whether on or off-prem, Azure, or AWS. IT only needs a single pane of glass to monitor and manage these environments while also allowing for IT and management to track related costs. Ultimately giving IT the agility of migrating between cloud platforms when needed. A use case for this would be a merger and acquisition of a company with a hybrid cloud environment. Cloud Foundation would help manage the complexities involved with integrating those resources into your own environment while maintaining security and the integrity of your current environment. VMware announced alongside the Cloud Foundation announcement at VMworld 2016 the new partnership with IBM Cloud. This allows companies to have choice in deploying SDCC whether it be on-prem in their own private data center(s) or with IBM. This solution is based with Cloud Foundation and allowing VMware customers to seamlessly extend private to public. Again, the software stack includes VMware vSphere, Virtual SAN, NSX, and VMware SDDC Manager. VMware SDDC Manager was announced back at VMworld 2015 and combined with Cloud Foundation is just the next step toward IoT with what VMware states as "Any Cloud, Any Application, Any Device". The SDDC Manager allows for a simplified management of a highly distributed architecture and resources. Cloud foundation integrates with the entire VMware stack which includes Horizon, vRealize Suite, vRealize Automation, vRealize Business, OpenStack and products like LogInsight. With Cloud Foundation natively integrating the software-defined data center stack and SDDC Manager, customers can flexibly upgrade individual components in the stack to higher editions allowing for flexibility in lifecycle management which consumes large amount of time in traditional IT. With Cloud foundation you can automate the entire software stack. Once the rack is installed and powered on with networking to the rack, the SDDC Manager takes the BOM that was built with your partner like Advizex, and includes user-provided environmental information like DNS, IP addresses, etc. to build out the rack. The claim is that this can reduce the provisioning time from weeks to hours which for those of you that have done this in a non-automated fashion can attest to how painful the process can be. When complete you have a virtual infrastructure ready to start deploying and provisioning workloads. In the complexities of traditional IT with silos, it takes extensive resources to provision a highly available private clouds, but with Cloud Foundation an administrator only needs to create and manage pools of resources decreasing the time to delivery of IT resources for consumption by the end-user whether it be a vm or a virtual desktop. This is done through a new abstraction layer called, Workload Domains. Workload Domains are a policy-driven approach for capacity deployment. Each workload domain provides the needed capacity with specified policies for performance, availability and security. An admin can create a workload for dev/test with a balanced performance and low availability requirement while also creating one for production with high availability and high performance. The SDDC Manager translates these policies into the underlying resources of compute which allows for the admin to concentrate on higher level tasks instead of spending time researching how to best implement. Lifecycle management introduces a lot of complexities which are typically manual process to patch and upgrade and can lead to issues within an infrastructure due to interoperability and configuration errors. In turn the validation and testing of these patches takes a lot of time away from an IT staff. Sometimes patches get deployed before they have been vetted correctly for security and other reasons or defer patches which can slow down the roll-out of new features, etc. SDDC Manager automates these tasks for both physical and virtual infrastructures. VMware tests all the components for the Cloud Foundation before shipping new patches to the customer. Within the lifecycle management of Cloud Foundation you can choose to apply the patches to just certain workloads or the entire infrastructure. SDDC can patch the vms, servers and switches while maintaining uptime thereby freeing resources to focus on business critical initiatives. Scalability is built into the platform within a hyper-converged architecture. You can start with a deployment as small as 8 nodes, and scale to multiple racks. Capacity can be added linearly in increments as small as one server node at a time within each rack allowing IT to align CapEx with business needs. Cloud Foundation automatically discovers any new capacity and adds it into the larger pool of available capacity for use. Some main use cases for Cloud Foundation are; Virtual Infrastructure allowing IT to expand and contract the underlying infrastructure to meet their changing business needs; IT Automating IT allowing IT accelerate the delivery and ongoing management of infrastructure, application and custom services, while improving overall IT efficiency; Virtual Desktop making VDI deployments faster and more secure. Administrators can focus on specifying the policies and needs of the VDI infrastructure instead of dealing with the details of deploying the VDI infrastructure. To learn more about VMware's Cloud Foundation you can visit the product page here.
You can also get hands-on with the product from the hands-on lab provided online from VMware. HOL-1706-SDC-5 - VMware Cloud Foundation Fundamentals |
RecognitionCategories
All
Archives
April 2024
|














 RSS Feed
RSS Feed