|
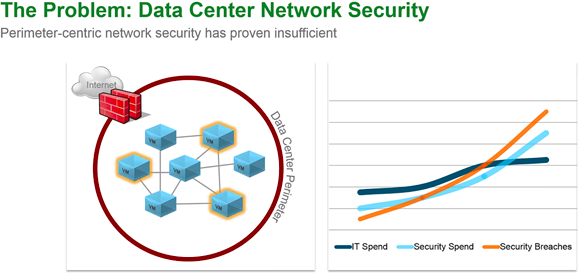
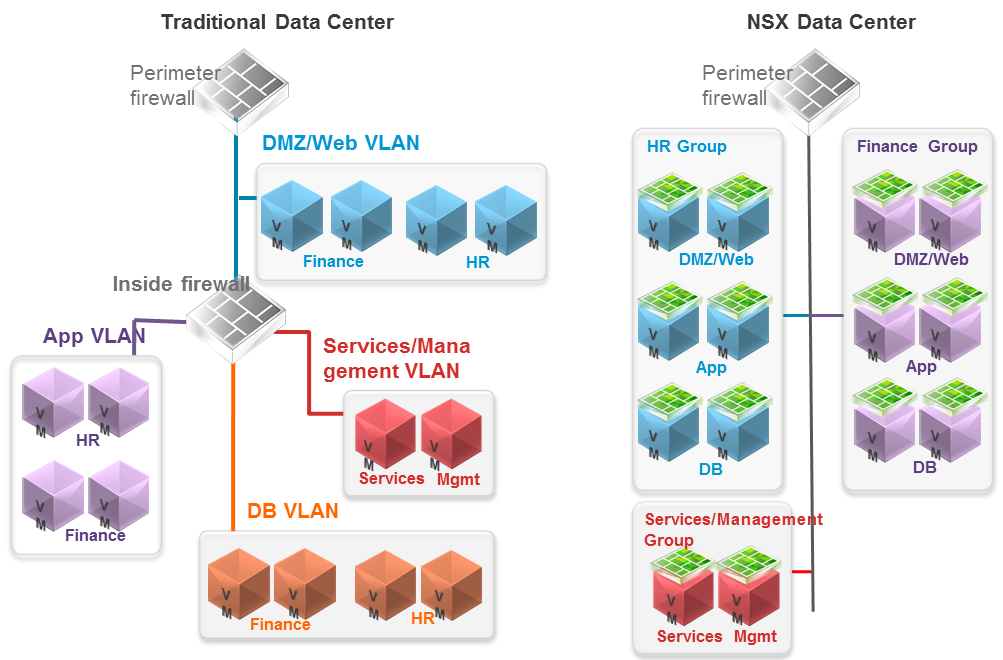
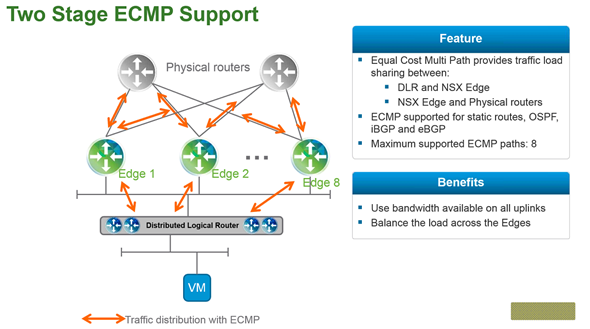
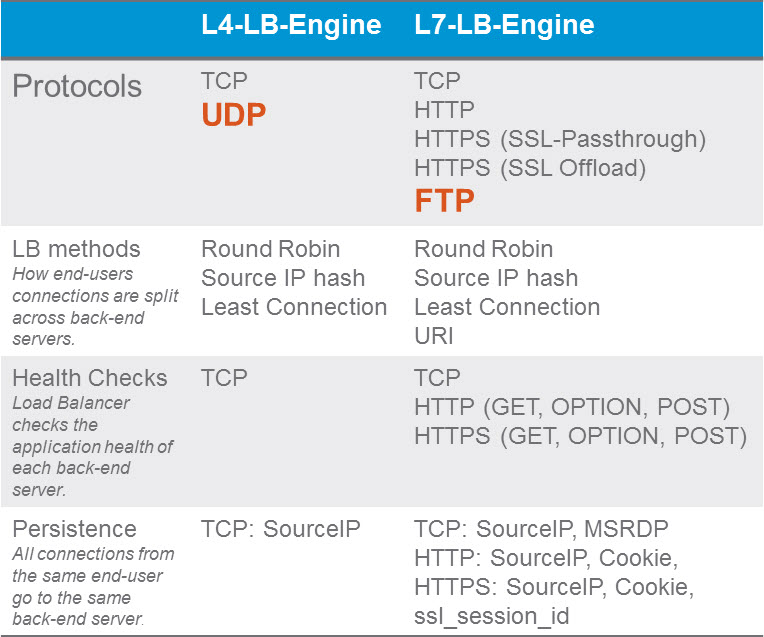
Segmentation It can be extremely difficult to secure and maintain security in your production environment. The traditional security model focuses on the perimeter defense but continued security breaches show that this model is not affective. Firewall can be deployed at each VM, but that proves to be unmanageable. With NSX 6.1 it is possible to micro segment your network, so that only traffic that is allowed can travel through the network between virtual machines. Traditionally, network segmentation is a function of a physical firewall or router, designed to allow or deny traffic between network segments or tiers. The traditional processes for defining and configuring segmentation are time consuming and highly prone to human error, resulting in a large percentage of security breaches. Implementation requires deep and specific expertise in device configuration syntax, network addressing, application ports and protocols. Network segmentation is a core capability of NSX. A virtual network can support a multi-tier network environment, meaning multiple L2 segments with L3 segmentation or micro-segmentation on a single L2 segment using distributed firewall rules. These could represent a web tier, application tier and database tier. Physical firewalls and access control lists deliver a proven segmentation function, trusted by network security teams and compliance. Confidence in this approach for cloud data centers, however, has been shaken, as more and more attacks, breaches and downtime are attributed to human error in to antiquated, manual network security provisioning and change management processes. In a virtual network, network services (L2, L3, ACL, Firewall, QoS etc.) that are provisioned with a workload are programmatically created and distributed to the hypervisor vSwitch. Network services, including L3 segmentation and fire-walling, are enforced at the virtual interface. Communication within a virtual network never leaves the virtual environment, removing the requirement for network segmentation to be configured and maintained in the physical network or firewall. Two Stage ECMP Equal cost multi path (ECMP) routing for distributed logical routers and NSX Edges has been added to 6.1. This gives NSX the ability to support ECMP between the Distributed Logical Router (DLR) and the NSX Edges to the physical network. This is limited to 8 ECMP paths. With this new feature you can better utilize bandwidth by way of multiple NSX Edges and their respective uplinks. Load Balancing Every NSX Edge has the ability to provide load balancing which can provide support for load balancing policies of IP hash, least connection, round robin and URI. NSX 6.1 includes the ability to load balance TCP, UDP and FTP. Firewall Enhancements
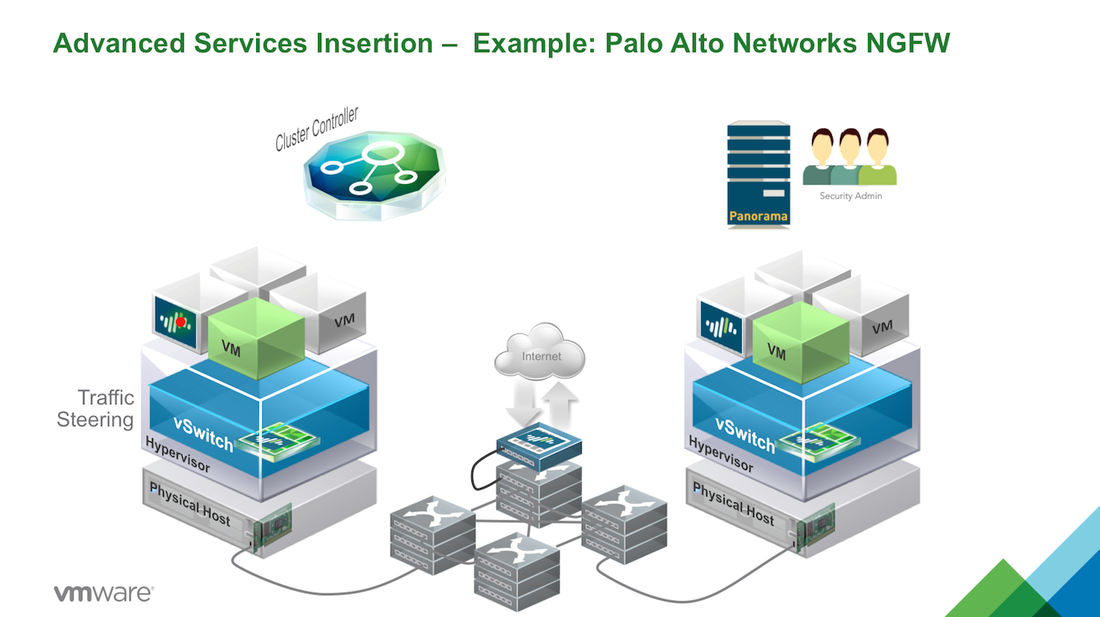
VMware NSX platform to distribute the Palo Alto Networks VM-Series next generation firewall, making the advanced features locally available on each hypervisor. Network security policies, defined for applications workloads provisioned or moved to that hypervisor, are inserted into the virtual network’s logical pipeline. At runtime, the service insertion leverages the locally available Palo Alto Networks next-generation firewall feature set to deliver and enforce application, user, context-based controls policies at the workloads virtual interface. VMware NSX provides a platform that allows automated provisioning and context-sharing across virtual and physical security platforms. Combined with traffic steering and policy enforcement at the virtual interface, partner services, traditionally deployed in a physical network environment, are easily provisioned and enforced in a virtual network environment, VMware NSX delivers customers a consistent model of visibility and security across applications residing on both physical or virtual workloads.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
RecognitionCategories
All
Archives
April 2024
|









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed